MailReport is an online platform (SaaS) that helps you to get and to keep the mechanisms up to date in order to prevent that anyone can send unauthorised emails on behalf of your organisation. This allows you to protect yourself of reputation damage caused by a
phishing attack. As an organisation, you don’t want to publish notices about emails allegedly sent on behalf of your company. MailReport makes your email visible and helps you to prevent phishing attacks on your domains.
MailReport processes the reports from the
DMARC standard and presents it in an easy to customise dashboard. This will give you a clear view of the legitimate and illegitimate email messages that were sent on behalf of your organization. MailReport gives you insight into any configuration errors of the mail server(s) and authentication mechanisms. MailReport helps you to get and control the required configuration. In addition, MailReport alerts if one of your e-mail servers appears on one of the many blacklists and keeps track of all the
DNS changes that are important for your email delivery.
MailReport provides the support you need on a daily basis and makes phishing attacks visible.
We do this by using the
DMARC standard and the authentication methods
SPF and
DKIM.
DMARC is a standard that is supported by all major technology companies like Google, Yahoo, Facebook and LinkedIn. The community of companies that are using the DMARC standard to prevent
phishing grows every day.
As a sender, you can publish a policy with
DNS. DMARC allows the following policy settings:
MailReport combined with
DMARC provides you with the following benefits. MailReport and DMARC:
MailReport provides you a unique insight into your email. You have the flexibility to customise the interface by:
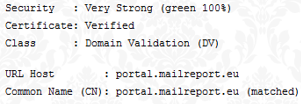
We take the security of our platform very seriously and we spend a lot of time and care to it. Our online platform is secured at the highest level.  For example, the
encryption of our site complies with two renowned tests (SSLLABS and Calomel) according to the latest guidelines. In addition, the
certificates of our site can not only be verified through the Certificate Authority, but also via
DNSSEC according to the new
DANE standard.
For example, the
encryption of our site complies with two renowned tests (SSLLABS and Calomel) according to the latest guidelines. In addition, the
certificates of our site can not only be verified through the Certificate Authority, but also via
DNSSEC according to the new
DANE standard.
In the area of privacy, our motto is: your data is your data.
We want to make it clear that we:
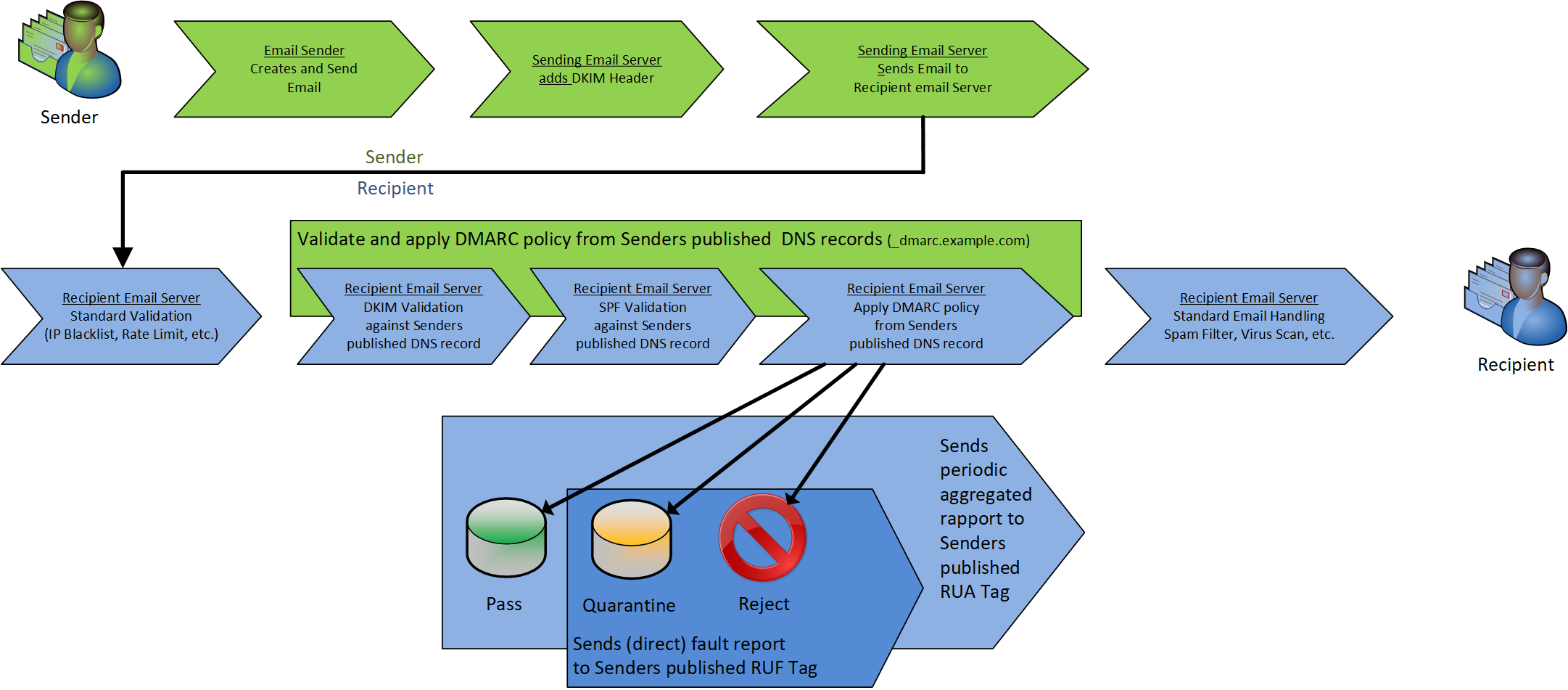
DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance. It is a technical specification to prevent email phishing at domain level. The standard was devised by a group of major technology companies including Google, Microsoft, Yahoo, Facebook, Paypal and Bank of America.
DMARC has been nominated as an open standard with the IETF under RFC-7489 and is about to be included in the 'apply or explain list' for the Dutch government.
What’s the goal of DMARC?
The goal of DMARC is to:
DMARC allows the sender to set a policy that tells the recipient how to handle incoming emails send as the sender’s domain when authentication of
SPF and/or
DKIM fails. The sender can publish this policy for the recipient by setting a DMARC record in
DNS.
The following policy settings can be specified: